Lorem ipsum
1
You have saved personalized supplements. Would you like to add them back to your cart?
£0.00 GBP
Your cart total must be £20.00 or more to proceed.
750mg
• Builds and repairs muscle tissue
• Promotes a healthy gut
• Improves cognitive function
Couldn't load pickup availability
 Vegan
Vegan
 Vegetarian
Vegetarian
 Non-GMO
Non-GMO
 GMP
GMP
 Gluten Free
Gluten Free
Glutamine is an amino acid, a fundamental building block of proteins, that plays an essential role in multiple functions within our body. While it is the most abundant amino acid in our muscles, its significance goes well beyond muscle health.

Muscle builder
Glutamine plays an intricate role in cellular metabolism. It's vital for repairing tissue and preventing muscle breakdown in the muscles, making it a staple for athletes and bodybuilders. In the gut, it acts as the primary fuel source for the intestinal lining cells. This ensures a robust gut lining, crucial for nutrient absorption and keeping harmful bacteria and toxins out of the bloodstream.
Moreover, during physical or mental stress, the body's requirement for glutamine can exceed its ability to produce it. Herein lies the importance of supplementation. Glutamine also aids in the production of glutathione, a potent antioxidant essential for immune health.
It's fascinating to note that the brain uses glutamine as a precursor to neurotransmitters, making it imperative for cognitive functions and maintaining mental equilibrium.
After consistent use, individuals may notice quicker recovery after workouts, fewer digestive issues, improved cognitive clarity, and a stronger immune response, especially during periods of stress or illness.
Take 1 capsule daily with food and water, unless specified otherwise on the sachet.
* Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet.
† Daily Value not established.
Vegetable capsule
Publications you might find interesting

1. Cruzat, V., Rogero, M. M., & Tirapegui, J. (2019). Effects of supplementation with free glutamine and the dipeptide alanyl-glutamine on parameters of muscle damage and inflammation in rats submitted to prolonged exercise. Cell biochemistry and function, 28(1), 24-30.
2. Kim, M. H., & Kim, H. (2017). The Roles of Glutamine in the Intestine and Its Implication in Intestinal Diseases. International journal of molecular sciences, 18(5), 1051.
3. Rao, R., & Samak, G. (2012). Role of Glutamine in Protection of Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junctions. Journal of Epithelial Biology & Pharmacology, 5(Suppl 1-M7), 47-54.
4. Lai, Y. N., Yeh, S. L., Lin, M. T., & Shang, H. F. (2004). Glutamine supplementation enhances mucosal immunity in rats with Gut-Derived sepsis. Nutrition, 20(3), 286-291.
5. Cruzat, V. F., Krause, M., & Newsholme, P. (2014). Amino acid supplementation and impact on immune function in the context of exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 11(1), 61.
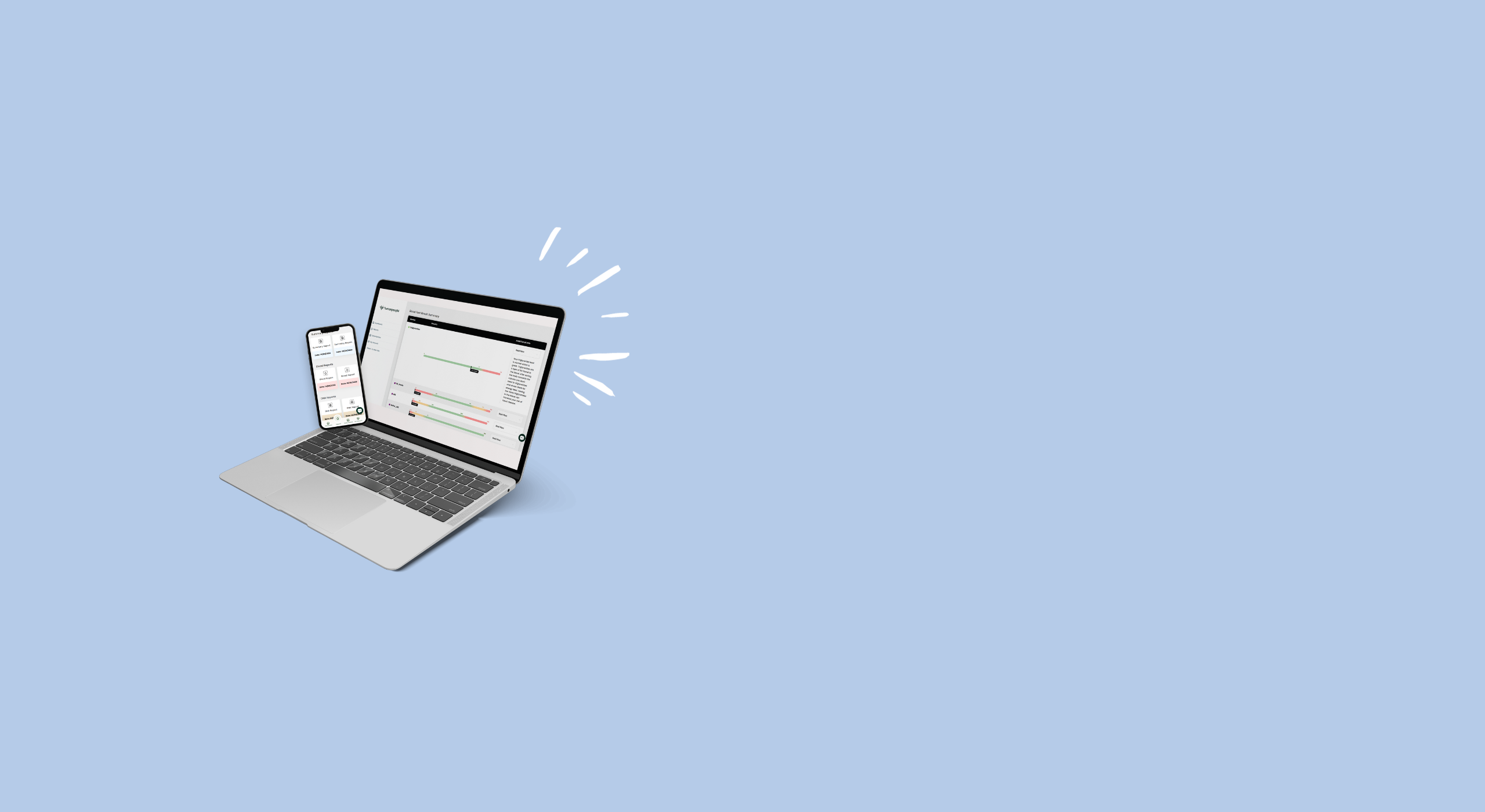

Gain access to your own data driven dashboard, health reports and personalised supplement plans.


• Supports cellular health and longevity
• Boosts NAD function
• Promotes skin health and elasticity

